Any use of products other than the permitted use without the express written authorization of Becton, Dickinson and Company is strictly prohibited.
Apoptosis is a normal physiologic process which occurs during embryonic development as well as in maintenence of tissue homeostasis. The apoptotic program is characterized by certain morphologic features, including loss of plasma membrane asymmetry and attachment, condensation of the cytoplasm and nucleus, and internucleosomal cleavage of DNA. Loss of plasma membrane is one of the earliest features. In apoptotic cells, the membrane phospholipid phosphatidylserine (PS) is translocated from the inner to the outer leaflet of the plasma membrane, thereby exposing PS to the external cellular environment. Annexin V is a 35-36 kDa Ca2+ dependent phospholipid-binding protein that has a high affinity for PS, and binds to cells with exposed PS. Annexin V may be conjugated to fluorochromes including APC. This format retains its high affinity for PS and thus serves as a sensitive probe for flow cytometric analysis of cells that are undergoing apoptosis. Since externalization of PS occurs in the earlier stages of apoptosis, APC Annexin V staining can identify apoptosis at an earlier stage than assays based on nuclear changes such as DNA fragmentation.
APC Annexin V staining precedes the loss of membrane integrity which accompanies the latest stages of cell death resulting from either apoptotic or necrotic processes. Therefore, staining with APC Annexin V is typically used in conjunction with a vital dye such as propidium iodide (PI) or 7-Amino-Actinomycin (7-AAD) to allow the investigator to identify early apoptotic cells (7-AAD negative, APC Annexin V positive). Viable cells with intact membranes exclude 7-AAD, whereas the membranes of dead and damaged cells are permeable to 7-AAD. For example, cells that are considered viable are both APC Annexin V and 7-AAD negative while cells that are in early apoptosis are APC Annexin V positive and 7-AAD negative, while cells that are in late apoptosis or already dead are both APC Annexin V and 7-AAD positive. This assay does not distinguish between cells that have undergone apoptotic death versus those that have died as a result of a necrotic pathway because in either case, the dead cells will stain with both APC Annexin V and 7-AAD. However, when apoptosis is measured over time, cells can be often tracked from APC Annexin V and 7-AAD negative (viable, or no measurable apoptosis), to APC Annexin V positive and 7-AAD negative (early apoptosis, membrane integrity is present) and finally to APC Annexin V and 7-AAD positive (end stage apoptosis and death). The movement of cells through these three stages suggests apoptosis. In contrast, a single observation indicating that cells are both APC Annexin V and 7-AAD positive, in of itself, reveals less information about the process by which the cells underwent their demise.
APC Annexin V is routinely tested by flow cytometric analysis. Other applications were tested at BD Biosciences Pharmingen during antibody development only or reported in the literature.
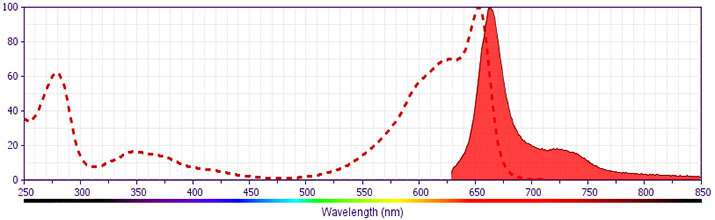
Allophycocyanin (APC), is an accessory photosynthetic pigment found in blue-green algae. Its molecular weight is approximately 105 kDa. APC has six phycocyanobilin chromophores per molecule, which makes it a very bright fluorochrome that is highly suitable for flow cytometry applications. Due to nearly identical excitation and emission properties but different spillover characteristics, APC and Alexa Fluor® 647 cannot be used simultaneously
温馨提示:因厂家更改产品包装、产地或者更换随机附件等没有任何提前通知,且每位咨询者购买情况、提问时间等不同,为此以下回复仅对提问者3天内有效,其他网友仅供参考!若由此给您带来不便请多多谅解,谢谢!
服务热线
0771-3293894